What is Decentralized? Understand the decentralized ecosystem behind crypto and Web3.
What is Decentralized? Understand the decentralized ecosystem behind crypto and Web3.
Decentralized refers to a system that operates without a central authority or control. It is a key foundation of blockchain technology and the Web3 world.
What is Decentralized?
A decentralized system is one that has no central point of control or management. Everyone in the network can freely participate, verify, and validate data without relying on a central authority such as a bank, government, or single organization.
The core principle of decentralization is distributing decision-making power and data storage away from a central point to multiple participants in the network. This ensures transparency, auditability, and reduces the risk of control or censorship by any single entity or organization.
In the world of cryptocurrency and Web3 technology, the concept of decentralization is fundamental because it allows users to truly own their assets, data, and digital identities—without the need for intermediaries.
Decentralization Concept

A decentralized system is designed to operate without central authority. Decision-making and data storage are distributed across multiple participants in the network, ensuring that no single entity can alter or control the system. All data is stored in multiple locations, allowing users to verify and validate information independently. This structure enhances transparency and security because there is no single point of failure that can be attacked or compromised.
In contrast, a centralized system is the traditional model where control is held by a single central authority. Users must rely on intermediaries to store data and process transactions. In a decentralized system, however, power is distributed across the network, allowing users to verify and participate in maintaining data integrity themselves.
For example, a central bank that manages money and transfers between accounts is a centralized system, whereas blockchain networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum are **decentralized systems**. Users can transfer cryptocurrency directly without going through a bank, and Web3 platforms allow individuals to directly own and control their own digital assets and data.
The difference between Centralized and Decentralized
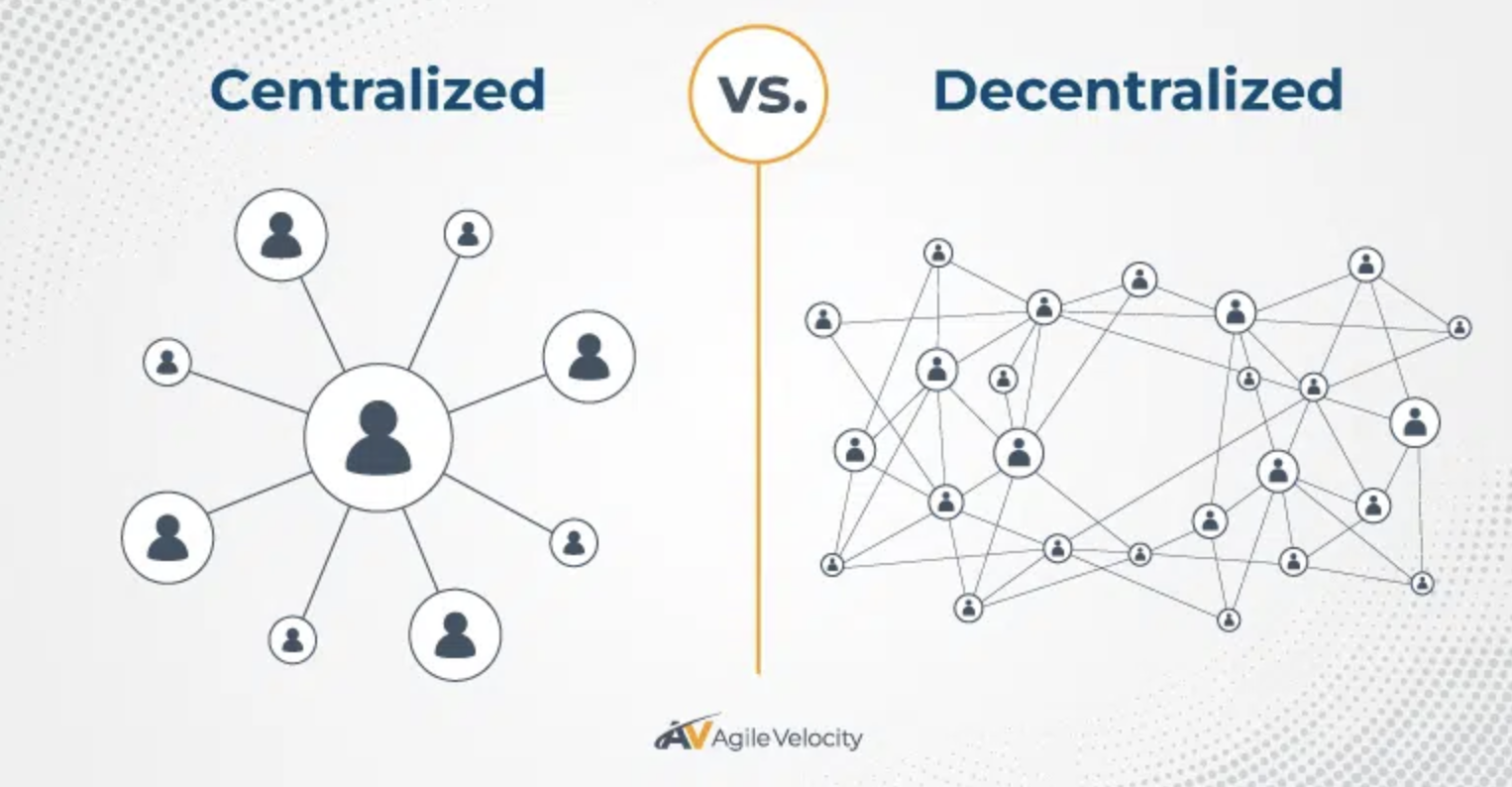
Image courtesy of agilevelocity
Centralized – Centralized Control
A centralized system is one where data and decision-making are managed by a single central authority or organization. All operations must go through this central entity, which is responsible for storing data, verifying accuracy, and controlling transactions. Users cannot modify or manage data independently — they must rely on the central authority for access and validation.
Examples of centralized systems:
-
Banks: Money transfers or deposits must go through a bank, which controls account data and authorizes transactions.
-
Social media platforms: All data and posts are stored and managed by the platform. Users do not directly own or control their data within the system.
Decentralized – Distributed Control
A decentralized system has no single central authority. Instead, data and decision-making are distributed among all users or nodes in the network. Each participant can verify the accuracy of data and help maintain the system’s security and integrity.
Examples of decentralized systems:
-
Bitcoin and Ethereum: Cryptocurrency networks where users can transfer funds and verify transactions without going through a bank.
-
Filecoin: A decentralized storage network that allows users to store or rent out storage space without relying on a central server.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Comparison Table
|
Aspect |
Centralized |
Decentralized |
|
Data Control |
A central authority has full control over all data. |
Data is distributed across the entire network. |
|
Security |
High risk of total system failure if the central authority is attacked. |
Highly secure because there is no single point of failure. |
|
Transparency |
Depends on the central authority’s willingness to disclose information. |
Transparent and every transaction can be verified. |
|
Transaction Speed |
Fast transactions since everything is managed by the central authority. |
May be slower because transactions must be verified collectively by multiple nodes. |
|
Flexibility |
Easy to manage since the central authority can make decisions independently. |
Requires consensus among multiple participants for decisions. |
Blockchain Technology and Decentralized Systems
Blockchain is the core technology that makes the concept of decentralization possible. It serves as the heart of decentralized systems by providing a structure where all participants in the network can access, verify, and validate information without relying on a central authority.
Distributed Ledger
One of the key features of blockchain is the Distributed Ledger system. Transaction data and records are stored in multiple copies across various nodes in the network. Each node can access and verify the data independently.
Key advantages of Distributed Ledgers:
-
High fault tolerance: Even if some nodes fail, the system continues to function.
-
Data reliability: Every change must be verified by multiple nodes, ensuring accuracy and trustworthiness.
Cryptography for Data Security
Blockchain uses cryptography to secure data and prevent tampering. Each block contains a unique hash — a digital signature that links it to the previous block. This means that altering one block would affect all subsequent blocks, making unauthorized changes virtually impossible. Cryptography also allows users to confidently verify transactions without needing a central authority.
Because of these features, blockchain has become the foundational technology behind cryptocurrencies and Web3, enabling users to truly own their digital assets, verify transactions independently, and participate directly in the network — all without intermediaries.
How a Decentralized Network Works
After understanding the core concept of decentralized systems, let’s explore how a decentralized system works, why it reduces reliance on intermediaries, and how it enhances user security.
Key Mechanisms of a Decentralized System
A decentralized network operates through three main mechanisms that work together:
1. Node
A node is a computer or device that participates in the network. Each node stores a copy of the system’s data and is responsible for verifying and relaying transactions to other nodes. This distribution of data across multiple points reduces the risk of data loss or attacks on a single point.
2. Consensus
Consensus is the process by which all nodes in the network agree on which transactions are valid before they are recorded on the blockchain. Consensus ensures that all nodes maintain consistent information, even without a central authority.
3. Validation
Validation involves multiple nodes simultaneously verifying the correctness of a transaction. For example, confirming that a digital asset or currency exists and has not been double-spent. A transaction is considered valid only when it has been confirmed by a predetermined number of nodes.
Example of Consensus Mechanism used in Decentralized Systems

Proof of Work (PoW) – Bitcoin
Nodes or miners must solve complex mathematical problems to create new blocks. This method requires high computational power but provides very strong security.
Proof of Stake (PoS) – Ethereum 2.0
Coin holders can lock their coins to validate transactions instead of using energy-intensive mining. This approach consumes less energy than PoW and processes transactions faster.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Coin holders elect delegates to validate transactions, making the system faster and more efficient. DPoS is suitable for networks that need to handle a high volume of transactions.
Benefits for Users
The combined operation of Nodes, Consensus, and Validation provides several advantages for users of decentralized systems:
-
Speed: Transactions can be processed instantly without relying on intermediaries such as banks.
-
Security: Storing multiple copies of data and using cryptography makes tampering extremely difficult.
-
Transparency: Every transaction can be verified, giving users confidence that the information has not been altered by any single party.
Benefits and advantages of a decentralized system
Advantages of Decentralized Systems
Decentralized systems offer several benefits compared to centralized systems:
-
No Intermediaries – Reduced Risk of Monopoly
Operating without a central authority reduces the risk of monopoly or control by a single organization. All users have equal rights to access and verify information. -
Enhanced Data and Transaction Security
Transaction data is stored in a distributed ledger and secured with strong cryptography, making it difficult to tamper with or alter information without network-wide approval. -
Transparency – Verifiable at Every Step
All transactions and records are written to the blockchain, allowing users to audit and verify them, ensuring a transparent and trustworthy system. -
Promotes Financial Freedom
Users can hold digital assets and conduct transactions independently, without relying on banks or central authorities. This is a fundamental principle of the cryptocurrency and Web3 ecosystem.
Limitations and Challenges of Decentralized Systems
Limitations and Challenges of Decentralized Systems
While decentralized systems offer many advantages, there are also limitations and challenges to consider:
-
Potentially Slower than Centralized Systems
Since transactions must be verified by multiple nodes across the network, processing can take longer than in centralized systems, where a single authority manages all data. -
High Energy and Resource Consumption
Some mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW), require significant computational power and energy, leading to high costs and, in some cases, environmental impact. -
Limited Understanding Among General Users
Decentralized systems and blockchain technology are complex, which may prevent everyday users from fully understanding how they work. This can affect adoption and confidence in using or investing in these systems. -
Unclear Regulations in Some Countries
Because decentralized systems are relatively new, many countries lack clear legal frameworks or regulations. Users may face legal risks or restrictions on usage in certain jurisdictions.
Real-world examples of decentralized systems
Decentralized systems are not just a technical concept, but are starting to be put into practice in many industries, allowing users to access various services without relying on a centralized entity.
In the finance (DeFi) industry

DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, is a digital financial system that operates without banks or central financial institutions. Users can carry out financial transactions directly with each other through Smart Contracts, which execute automatically and are verifiable.
Decentralized Exchange (DEX) platforms, such as **Uniswap** and **PancakeSwap**, enable users to trade cryptocurrencies directly. The system automatically manages liquidity and matches buy and sell orders.
In the world of art and NFTs

Decentralization is applied in digital art and NFT (Non-Fungible Token) marketplaces, enabling creators to sell their work directly while clearly proving ownership.
Marketplaces like OpenSea use Smart Contracts to verify ownership and transfer of NFTs. All transaction data is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and auditability.
Additionally, artists can automatically receive royalties each time their work is resold, providing ongoing income and reducing the risk of fraud.
In the world of Web3 and DAO

One of the key tools of Web3 is the DAO, a type of organization that differs significantly from traditional organizations because there is no single owner or central authority controlling everything.
Decisions in a DAO are made through votes by members holding tokens, where each token usually represents a voting right. Members can propose new ideas or projects, and every proposal must be approved by the network vote to take effect.
Additionally, all DAO activities are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency, auditability, and reducing the risk of fraud or external interference.
Why Decentralized Systems Matter for the Future of Crypto
1. Core Structure of Web3
Decentralized systems are at the heart of Web3, the next evolution of the internet. In the current Web2 world, most data is stored and controlled by large companies such as Google, Facebook, or X, which manage the entire platform.
In Web3, the system shifts away from reliance on intermediaries, allowing users to truly own their own data.
2. Enhances Transparency and Reduces Centralized Control
One of the strongest advantages of decentralized systems is transparency. All transactions and data are recorded on the blockchain, a public ledger that can be audited at any time.
The lack of a central authority also reduces risks of interference, such as account blocking, transaction control, or privacy violations. Moreover, decentralization helps prevent internal fraud because all changes require validation by multiple parties, making processes fair and auditable.
Examples of Projects Driving Decentralization
-
Bitcoin: The first example of a decentralized financial system with no central bank or controlling entity; all transactions are validated by miners worldwide.
-
Ethereum: Builds on decentralization with Smart Contracts, enabling developers to create decentralized applications (DApps).
-
Polkadot: Focuses on connecting different blockchains to allow crypto ecosystems to operate together efficiently.
-
Filecoin: Applies decentralization to data storage, allowing users to share their storage space for others to rent without relying on any single cloud service provider.
KuCoin Thailand with Decentralized System

KuCoin Thailand is a cryptocurrency trading platform that fully supports **decentralized digital assets**, including popular coins like **Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), TRON (TRX)**, as well as Web3 tokens and DeFi or DAO projects. Users can trade a wide range of assets in one place, making portfolio management convenient and comprehensive.
Start trading decentralized coins today at KuCoin Thailand
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Decentralized Systems
Q1: What is a Decentralized system, and how is it different from Centralized?
A decentralized system has no central authority controlling data; decision-making is distributed across all nodes. This ensures transparency, security, and reduces the risk of control by any single party.
In contrast, a centralized system is controlled by a single organization or authority, which manages all data and decisions.
Q2: How does blockchain make decentralized systems secure?
Blockchain uses a Distributed Ledger to record all transactions publicly and applies cryptography to secure the data. This prevents information from being altered or falsified without network-wide validation.
Q3: Are there limitations to decentralized systems?
Key limitations include:
-
Transactions may be slower than centralized systems.
-
High energy and resource consumption, especially with Proof of Work (PoW).
-
General users may find the system complex and difficult to understand.
-
Regulations in some countries are still unclear.
Q4: Can decentralized systems be used in traditional businesses?
Yes. Traditional businesses can adopt decentralized systems for:
-
DeFi solutions
-
Distributed data storage
-
Creating DAOs for internal decision-making
-
Transparent voting systems
These applications reduce intermediaries and increase trust.
Q5: Examples of coins and platforms using decentralized systems
-
Bitcoin (BTC)
-
Ethereum (ETH)
-
Polkadot (DOT)
-
Filecoin (FIL)
-
Solana (SOL)
Summary – What is Decentralized and Why Does it Matter for the Digital Future?
A decentralized system refers to a structure without a central authority, where data and decision-making are distributed across all users or nodes. This creates transparency, security, and reduces the risk of monopoly or control by a single organization.
Technologies like blockchain and mechanisms such as consensus make decentralized systems reliable, allowing transactions to be audited, preventing tampering, and building user trust. At the same time, they enable new innovations such as **DeFi, DAO, Web3**, and other decentralized applications.
With these features, decentralized systems form a fundamental foundation for the modern digital economy and financial world, emphasizing transparency, participation, and financial freedom for all users.
⚠️ Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency and digital token involve high risks; investors may lose all investment money and should study information carefully and make investments according to their own risk profile.
KuCoin Thailand
(Operated by ERX Company Limited)
Email: happy@kucoin.th
- Website: www.kucoin.th
- Facebook: facebook.com/KuCoinThailand
- Facebook Community Group: facebook.com/groups/kucointhailandcommunity
- LINE Official Account: @KuCoinThailand
- Instagram: Kucointhailand
- X (formerly Twitter): x.com/KuCoinThailand
- Telegram: @KuCoinTH_Official
📲 Download the KuCoin Thailand app today!
👉 Click here to download Available now on both the Thailand App Store and Play Store.