Polygon (POL): What Is It? How Polygon 2.0 Enhances Ethereum’s Performance
Polygon (POL): What Is It? How Polygon 2.0 Enhances Ethereum’s Performance
Polygon (POL) is a blockchain network designed to help Ethereum operate faster, with lower fees, and with the potential to be a strong long‑term investment.
What is Polygon (POL) ?

Polygon is a blockchain network built to help Ethereum operate faster with lower transaction fees.
Since Ethereum is a highly popular blockchain, transactions on the network can sometimes be slow and costly. Polygon solves this by using Layer 2 technology, allowing users to transfer funds, trade NFTs, or use various applications more quickly and at a lower cost.
Polygon (POL) is closely integrated with Ethereum, enabling apps or projects built on Ethereum to easily migrate to Polygon while maintaining Ethereum’s security standards—only with increased speed and reduced expenses. This makes Polygon a popular choice for both developers and users, whether beginners or professionals, especially for building DeFi applications, NFTs, or other decentralized apps (DApps).
Polygon's origins and development team
Polygon originated from a project called Matic Network, which was created to solve common issues faced by Ethereum users—namely slow transactions and high fees. The Polygon team consists of Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, and Anurag Arjun, each bringing expertise in blockchain, digital finance, and decentralized technology. Together, they built a platform that enables Ethereum to support a large number of users efficiently without compromising network security or reliability.
In its early phase, Polygon was known as Matic Network and focused on developing Layer 2 scaling technology for Ethereum. This technology helps speed up transactions and reduce fees, enabling developers to build practical, cost-effective dApps for everyday users.
As the network grew and demand for cross-chain interoperability increased, the team expanded Matic Network into what is now Polygon Network.
This shift was not just a name change—it represented a major technological advancement. Polygon evolved into a multi-chain ecosystem that not only supports Layer 2 scaling for Ethereum but can also connect and interoperate seamlessly with other blockchains.
This allows developers and users to build a wide variety of applications—DeFi, NFTs, and other dApps—on a single network while still enjoying fast transaction speeds and low fees.
How does Polygon work?
Polygon functions as a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum. The term Layer 2 scaling refers to an additional layer built on top of Ethereum to help process transactions faster and at lower cost. Instead of performing every transaction directly on Ethereum, Polygon processes a portion of the transactions on its own network and then sends the final results back to Ethereum.
Polygon operates using a combination of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and the Plasma Framework.
PoS allows POL holders to stake their tokens to help validate transactions and secure the network, enabling anyone to participate and earn rewards.
The Plasma Framework enables Polygon to create “Polygon chains” or sub-chains designed to handle large volumes of transactions without slowing down Ethereum.
Their interaction can be summarized like this:
User transaction → Polygon chain → Final results submitted back to Ethereum
Polygon's core technology

ขอบคุณภาพจาก polygon.technology
Polygon uses several technologies together to help Ethereum operate faster and at lower cost. These tools are the core technologies that enable Polygon to function smoothly.
Polygon SDK
A toolkit for developers that makes it easy to build new applications and chains on Polygon without starting from scratch. Developers can design their own Layer 2 solutions or multi-chain ecosystems as needed.
Plasma Chain
A technology that creates child chains to process large volumes of transactions quickly while still relying on Ethereum’s security.
zk-Rollups
A method that bundles multiple transactions into a single rollup and then submits the results back to Ethereum, enabling faster processing and reducing the amount of data stored on the blockchain.
Validium
Similar to zk-Rollups, but the data is stored off-chain. This enables extremely fast processing and supports very high transaction volumes—ideal for applications that require speed.
Sidechains & Bridges
These technologies connect Polygon with Ethereum and other blockchains.
-
Sidechains handle transaction processing
-
Bridges transfer data and assets across networks
What is POL Coin and what role does it play in the ecosystem?
MATIC was the native digital token of Polygon, created to power the entire network ecosystem. It has been upgraded to POL now. It serves several important functions, including the following:
1. Paying Transaction Fees (Gas Fees)
When performing transactions, transferring funds, trading NFTs, or using applications on Polygon, POL is used to pay gas fees. Using POL enables faster transactions at significantly lower costs compared to operating directly on Ethereum.
2. Staking and Governance
Token holders can stake POL to help secure the network and earn additional POL as rewards. For governance, POL holders can participate in voting on key decisions within the network—such as upgrades or protocol changes—allowing users to play an active role in the ongoing development of Polygon.
Supply and Tokenomics
Currently, POL has a fixed maximum supply, which helps control inflation. However, a portion of new tokens is still released according to the network’s development plan. This allows POL to be useful both for practical use within the ecosystem and as a long-term investment.
Max Supply: 10,000,000,000 POL
Circulating Supply: ~4,877,830,774 POL
POL Coin Allocation
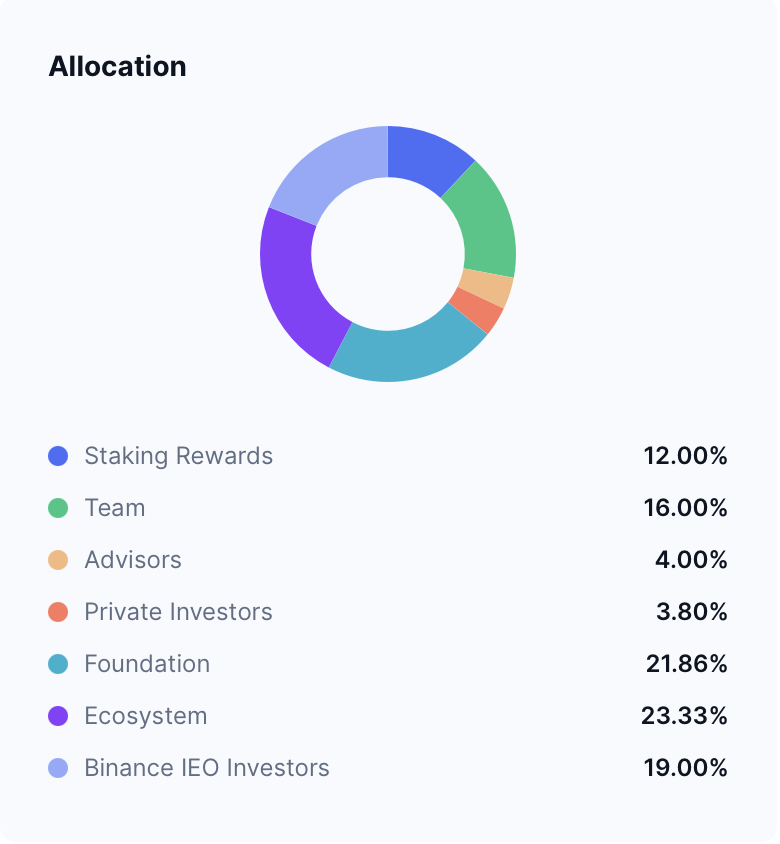
ขอบคุณภาพจาก coinmarketcap
POL tokens are released into circulation gradually to match the expansion of the network. Additionally, some POL is burned through the EIP-1559 mechanism—similar to Ethereum—to help maintain a balanced token supply.
When network activity increases, more tokens are burned. This reduces the overall supply, contributing to greater scarcity and potentially increasing the token’s long-term value.
Comparing Polygon to other networks
Even though Polygon was created to enhance Ethereum’s capabilities, there are other blockchain networks in the ecosystem with similar goals—such as Ethereum, BNB Chain, and Avalanche. Each network has its own strengths, weaknesses, and unique design approaches.
Ethereum
One of the most popular blockchain networks in the crypto world, known for its strong smart contract infrastructure and the largest developer community. However, Ethereum’s limitations include slow transaction speeds and high fees.
Polygon
Built specifically to solve Ethereum’s scalability issues. It functions as a Layer 2 solution connected to Ethereum, enabling faster and cheaper transactions while still benefiting from Ethereum’s high security standards.
BNB Chain
Developed by Binance, it stands out for extremely low fees and fast transaction speeds—making it suitable for general users. However, it is more centralized due to having fewer validators.
Avalanche
A network focused on very high speed and the ability to create customized subnets, making it suitable for diverse applications. It can process a large number of transactions per second, though its fees are slightly higher than Polygon’s.
Comparison Table: Polygon vs Ethereum vs BNB Chain vs Avalanche
|
Feature |
Polygon (POL) |
Ethereum (ETH) |
BNB Chain (BNB) |
Avalanche (AVAX) |
|
Network Type |
Layer 2 / Sidechain for Ethereum |
Layer 1 Blockchain |
Layer 1 Blockchain |
Layer 1 Blockchain |
|
Consensus Mechanism |
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) |
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) |
Proof-of-Staked Authority (PoSA) |
Avalanche Consensus |
|
Transaction Speed (TPS) |
~7,000 TPS |
~30 TPS |
~300 TPS |
~4,500 TPS |
|
Transaction Fees (Gas Fee) |
Very low (< $0.01) |
High (sometimes > $5) |
Low (~$0.05) |
Medium (~$0.1–$0.3) |
|
Security |
Inherits Ethereum security |
Very high |
Medium (some centralization) |
High |
|
Ecosystem |
Fast-growing, many DApps & DeFi |
Largest in the world |
Fast-growing, strong Binance-backed projects |
Focused on DeFi & Subnets |
Overall, Polygon stands out for its high transaction speed and extremely low fees, while still benefiting from Ethereum’s security. This makes it an excellent choice for both developers and everyday users who want a fast and cost-efficient experience.
Ethereum, on the other hand, remains the most trusted and established blockchain network, even though its transaction fees are higher than many alternatives.
BNB Chain excels in ease of use and its ecosystem, which is powered by Binance—helping new projects grow quickly. Avalanche’s strengths lie in its speed and flexible architecture, making it suitable for DeFi projects and applications that require high performance.
What Can Polygon Be Used For?
Polygon is not just an enhancement for Ethereum; it is a large ecosystem that supports many types of applications—from DeFi and GameFi to NFT marketplaces with millions of users worldwide.
dApps on Polygon
Polygon enables decentralized applications (dApps) to operate quickly with low fees while still inheriting Ethereum-level security. This has made Polygon a major hub for DeFi, GameFi, and NFT projects today.

Polygon hosts many well-known applications, such as:
Aave
A top DeFi platform that allows users to securely deposit and borrow crypto assets, with fees significantly lower than on Ethereum.
QuickSwap
A decentralized exchange (DEX) similar to Uniswap, but with faster and more cost-efficient transactions.
OpenSea
A global NFT marketplace that supports Polygon, enabling artists and collectors to create and trade NFTs without paying high gas fees.
In addition, the Polygon ecosystem is filled with popular DeFi, GameFi, and NFT marketplace projects such as SushiSwap, Curve, Balancer, Pegaxy, Planet IX, and Magic Eden. These platforms choose Polygon because of its high transaction throughput and extremely low fees—ideal for applications that require a large number of daily transactions.
Latest Polygon Ecosystem
Polygon is currently evolving into Polygon 2.0, focusing on building a multi-chain Layer 2 ecosystem where each chain within Polygon can transfer data and assets to one another seamlessly.
Polygon also includes several major projects, such as:
-
Polygon zkEVM: A fully Ethereum-compatible Zero-Knowledge Rollup technology
-
Polygon ID: A decentralized identity verification system
-
Polygon CDK (Chain Development Kit): A toolkit that allows developers to build their own Layer 2 blockchains on Polygon more easily
Latest Update: Polygon 2.0 and the Transition from POL to POL
In 2024, Polygon announced a major upgrade under the name Polygon 2.0, marking a key step in transforming its architecture from a traditional Layer 2 system into a full multi-chain ecosystem. The goal is for every chain built on Polygon to connect and interact seamlessly under one unified framework.
Polygon 2.0 Summary
ขอบคุณภาพจาก polygon.technology
Polygon 2.0 is designed to create a fully interconnected Layer 2 ecosystem, powered by zkEVM (Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine). This technology provides Ethereum-level security while delivering extremely fast transaction processing and very low fees.
Polygon has also introduced a new Protocol Layer that enables communication between chains within the Polygon ecosystem. This allows each chain to exchange data or assets without intermediaries—an important step toward the “Internet of Value,” where cross-chain digital asset transfers are smooth and effortless.
Difference Between MATIC and POL
One of the most significant changes in Polygon 2.0 is the transition from MATIC to POL as the main token.
-
MATIC was the original Polygon token, used for transaction fees (gas), staking, and governance on the main network.
-
POL is designed as a next-generation token capable of multi-chain staking, securing multiple chains across the Polygon ecosystem at the same time.
In simple terms, POL is the upgraded version of MATIC, with more functionality. It is not limited to a single chain—POL can secure and operate across multiple Polygon chains simultaneously.
Impact on Token Holders
For existing MATIC holders, there is no need to worry. Polygon designed the upgrade to be user-friendly. Holders can swap MATIC to POL at a 1:1 ratio through Polygon’s official platform.
Key points:
-
Staking and governance rights will migrate to POL.
-
The expanded ecosystem provides more growth potential for the token as multi-chain usage increases.
-
In the long term, POL will fully replace MATIC as the primary token of the Polygon 2.0 network.
Is Polygon a Good Investment? (2025 Outlook)
Growth Opportunities in DeFi and Web3
Many analysts believe that Polygon’s transition to Polygon 2.0 and the adoption of zkEVM significantly increases its real-world utility—especially in DeFi, NFTs, and applications requiring high transaction volumes.
-
Oak Research reported an increase in Polygon’s TVL in 2025, indicating growing network usage.
-
Binance Research noted that Polygon’s upgrades and institutional support enhance growth potential for POL, although they also warn about short-term price volatility.
Bullish Factors and Risks
Bullish factors often mentioned by analysts include:
-
The transition from MATIC to POL
-
zk-Rollups / zkEVM compatibility with Ethereum
-
Polygon’s rapidly expanding ecosystem
These factors increase utility and help reduce competitive pressure.
However, widely noted risks include:
-
Competition from other Layer 2 networks like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base
-
Overall instability of the crypto market
-
Technical and real-world adoption risks
Analysts from major crypto sites, including CoinDesk and CoinMarketCap, commonly conclude that although Polygon has strong technological fundamentals, its price is still significantly influenced by sentiment and broad market acceptance.
Analysts’ Perspectives
-
Benzinga forecasts that POL could appreciate in 2026, with projected prices between $0.50–$0.60 if development progresses as planned. They caution that failure to expand the ecosystem as expected could lead to price declines due to macro conditions and user adoption risk.
-
CoinCodex predicts POL’s 2025 price range at $0.136–$0.195, noting a bearish sentiment due to slower-than-expected ecosystem expansion. This aligns with chart analysis from altFINS, which finds POL in a downtrend.
Polygon (POL) Coin Storage

For Polygon (POL) holders, securing your tokens is essential because cryptocurrencies must be stored in a digital wallet, or crypto wallet. These wallets come in two main types: Hot Wallets and Cold Wallets.
Comparison Table: Hot Wallet vs Cold Wallet
|
Category |
Hot Wallet |
Cold Wallet |
|
Connection |
Always online and connected to the internet |
Offline, not connected to the internet |
|
Security |
Moderate security; vulnerable to hacks if the device is infected with malware |
Highest security because it is not connected online |
|
Ease of Use |
Very easy to use; allows instant transfers and dApp connections |
Requires plugging in a device or using specific apps; ideal for long-term holding |
|
Ideal For |
General users and investors who trade or transfer frequently |
Long-term investors who hold large amounts of crypto |
|
Popular Examples |
MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet |
Ledger Nano X, Trezor, SafePal S1 |
How to Store POL Safely
-
Avoid keeping tokens on exchanges for too long:
Exchange wallets are suitable only for short-term trading. They can be vulnerable to hacks and may lead to loss of all funds. -
Use Hot Wallets for daily activities:
Such as transferring tokens, using DeFi apps, or interacting with NFT platforms. -
Use Cold Wallets for long-term holding (HODLing):
They are more secure and recommended for storing large amounts of crypto. -
Backup your Seed Phrase securely:
Do not store it on your phone or take photos saved to the cloud. Write it down on paper or keep it in an offline storage device. -
Always update your wallet software:
This helps protect against vulnerabilities and potential attacks.
Wallets That Support Polygon
Polygon (POL) is supported on both Ethereum (ERC-20) and Polygon Mainnet, so always check which network a wallet supports before transferring tokens.
Popular wallets that support Polygon include:
-
MetaMask: Popular for DeFi and dApps; easy to connect to Polygon
-
Trust Wallet: Mobile-friendly and supports both MATIC (ERC-20) and Polygon Network
-
Ledger / Trezor: Hardware wallets (Cold Wallets) for maximum security
-
Coinbase Wallet: Supports Polygon chain and can connect directly to dApps
-
SafePal: A hybrid wallet with both hot and cold features, mobile-friendly
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Polygon
Q1. How is Polygon different from Ethereum?
Polygon is a scaling solution for Ethereum that speeds up transactions and lowers fees while still connected to Ethereum’s security. Ethereum is the main Layer 1 network used to build and run smart contracts.
Q2. How does the Polygon Chain work?
Polygon uses Layer 2 scaling technology that processes large numbers of transactions off Ethereum before sending summarized data back to the main chain.
Q3. Are Polygon and MATIC the same?
MATIC is the original token of the Polygon network used for gas fees, staking, and governance. Polygon is now upgrading to a new token called POL as part of Polygon 2.0.
Q4. Does Polygon have a future?
Many analysts believe Polygon has strong potential because it plays a major role in Web3, GameFi, and DeFi, and has partnerships with global companies such as Starbucks, Reddit, and Nike. However, future price movements depend on the success of Polygon 2.0 and overall crypto market conditions.
Q5. What can Polygon be used for?
Polygon is used to build and connect decentralized applications (dApps) such as DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, blockchain games, and Web3 applications like Aave and QuickSwap.
Summary: What Is Polygon?
Polygon (POL) is a project designed to enhance the performance of the Ethereum network. It functions as a Layer 2 Scaling Solution that increases transaction speed, reduces fees, and expands Ethereum’s capabilities for broader use.
Polygon is not only a support network for Ethereum—it has grown into a full blockchain ecosystem covering DeFi, GameFi, NFT applications, and real-world enterprise use cases.
With continuous innovations such as Polygon 2.0, along with a strong and active developer community, Polygon has become one of the most important Layer 2 networks driving the Ethereum ecosystem and the future of Web3 toward real-world adoption.
⚠️ Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency and digital token involve high risks; investors may lose all investment money and should study information carefully and make investments according to their own risk profile.
KuCoin Thailand
(Operated by ERX Company Limited)
Email: happy@kucoin.th
- Website: www.kucoin.th
- Facebook: facebook.com/KuCoinThailand
- Facebook Community Group: facebook.com/groups/kucointhailandcommunity
- LINE Official Account: @KuCoinThailand
- Instagram: Kucointhailand
- X (formerly Twitter): x.com/KuCoinThailand
- Telegram: @KuCoinTH_Official
📲 Download the KuCoin Thailand app today!
👉 Click here to download Available now on both the Thailand App Store and Play Store.



